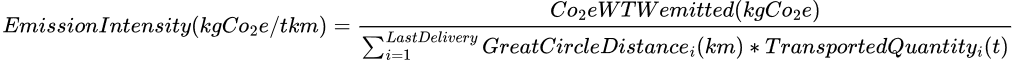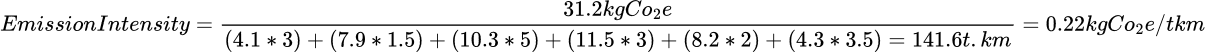Introduction
The purpose of this page is to explain the allocation method in accordance with the international recommended guidelines described in the GLEC framework.
The goal of this method is to distribute the emissions emitted during a trip between the various stops.
Requirements
To apply this process, it is required to know:
- The total emissions emitted during the trip
- The loading and unloading at each stop of the trip
- The entire trip must be taken into account, from the vehicle's departure to its return to the depot. The last waypoint must always be the depot or the final end of the trip.
Allocating emissions
To fairly divide the emissions generated during a depot-based pickup and delivery roundtrip, the allocation method uses two criteria to compute a "notional transport performance" for each order:
- The distance (km) between the depot and each order: for road transportation, it is recommended to use the Shortest Feasible Distance (SFD). SFD represents the shortest practical route between two places and can be calculated using e.g. PTV Developer Routing API. Another simple option is to use the Great Circle Distance (GCD). In practice, using GCD is less accurate but the differences between the two options are relatively small. For the demonstration, we will use GCD in the calculations below.
- The quantity: The sum of what has been loaded and unloaded during the stop. This quantity can be either a volume (m3) or a weight (t)
Then, the assignment of emission values to every order is carried out as follows:
- A notional transport performance (in t.km) is determined as the product of the distance and the quantity.
- These notional transport performances of all orders of the trip are added up.
- For each order, its share (in %) of the sum of the notional transport performances is determined.
- According to these shares the emission values of the entire trip are distributed to the stop / orders.
Great Circle Distance
To measure the distance between the depot and a pickup/delivery point, the method is using below the great circle distance (also called orthodromic or spherical distance). It is the shortest distance between two points on the surface of a sphere.
For a depot (longitudeA,latitudeA) and a delivery point B (longitudeB, latitudeB):
R is the terrestrial radius (~6371 km)
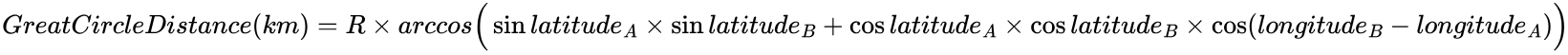
This formula is known as the Haversine formula.
Emission Intensity
When reporting greenhouse gas emissions, it's essential to calculate the emission intensity, a measure of the greenhouse gas emissions per unit of freight transported. It is expressed as the amount of CO₂ equivalent (kg CO₂e) emitted per ton-kilometer (t·km) of freight transported. It provides a standardized way to compare the environmental performance of transport operations.
In our example it is calculated by dividing the total Well To Wheel CO2 emitted during the trip, by the sum of all the depot-stop GCD distances multiplied by the respective shipment weight of the stops: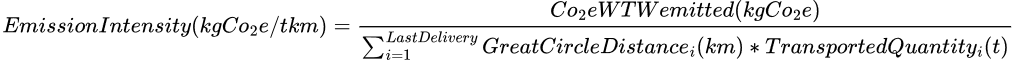
Example: 6-stops trip
In this example, the vehicle served 6 pickup and/or delivery points, before returning to the depot.
- The vehicle is deposited in the same place on departure and arrival.
- The vehicle starts from the depot with an initial load of 8t.
- A fuel consumption of 8L is measured, with
GASOLINEfuel type. - The great circle distance (in green) is computed between the depot and every stop.
- The quantity of goods (here the quantity is a weight in t) that were loaded and unloaded during the trip are reported for every stop.
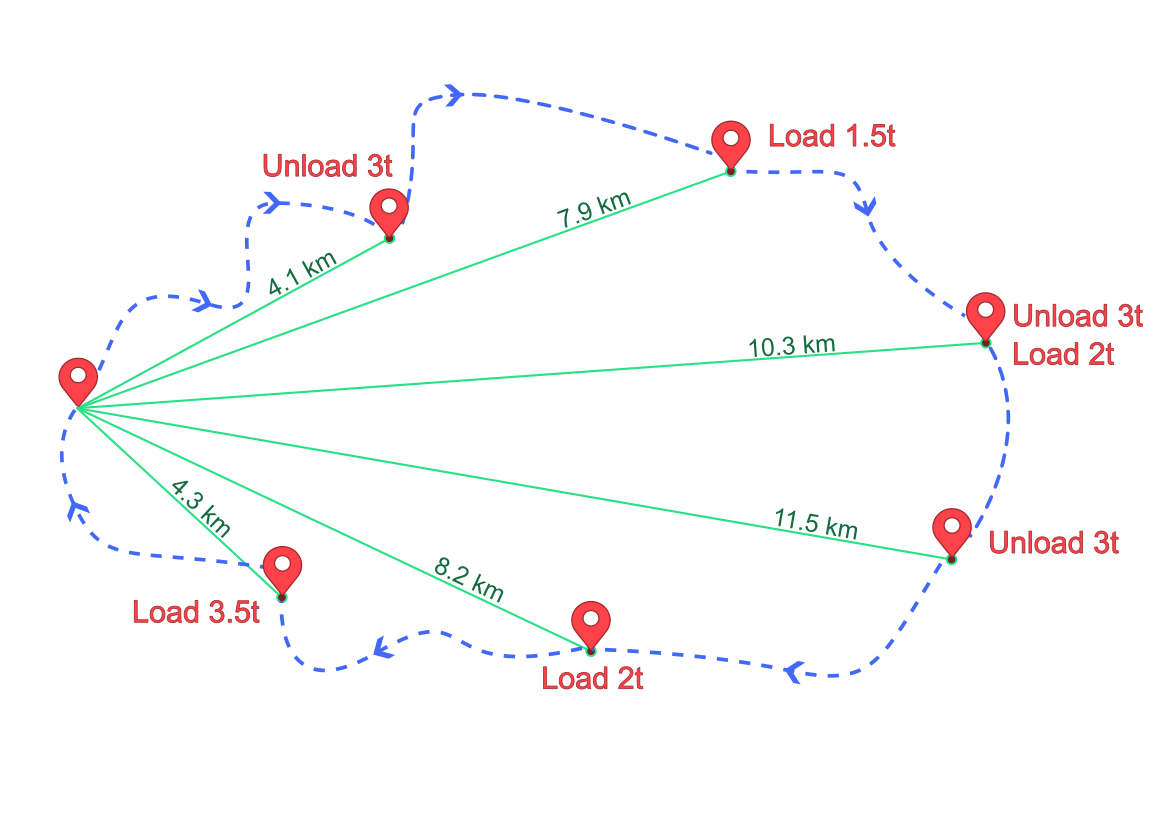
For each stop, compute the notional transport performance :
| Order | Great circle distance (km) | Quantity ( unload + load weight t) | Notional transport performance (t.km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Order 1 | 4.1 | 3 | 12.3 |
| Order 2 | 7.9 | 1.5 | 11.85 |
| Order 3 | 10.3 | 3 + 2 | 51.5 |
| Order 4 | 11.5 | 3 | 34.5 |
| Order 5 | 8.2 | 2 | 16.4 |
| Order 6 | 4.3 | 3.5 | 15.05 |
The sum of all notional transport performances is 12.3 + 11.85 + 51.5 + 34.5 + 16.4 + 15.05 = 141.6 t.km
Then, for each stop, compute the share (%) of the sum of all notional transport performances.
| Order | Share (%) |
|---|---|
| Order 1 | 8.69 |
| Order 2 | 8.37 |
| Order 3 | 36.37 |
| Order 4 | 24.36 |
| Order 5 | 11.58 |
| Order 6 | 10.63 |
Select a standard to generate an emissions report for the trip. With the standard ISO14083_2023 emission factors, a GASOLINE fuel type, the PTV Developer Routing API indicates that 26.24 kg CO2e TTW and 31.2 kg CO2e WTW were emitted during the trip, for a fuelConsumption of 8L. With the total emissions, use the previously computed order's shares and the total emitted emissions to compute the CO2e emissions of each order.
| Order | CO2e emissions Tank To Wheel (kg CO2e) | CO2e emissions Well To Wheel (kg CO2e) |
|---|---|---|
| Order 1 | 2.28 | 2.71 |
| Order 2 | 2.20 | 2.61 |
| Order 3 | 9.54 | 11.35 |
| Order 4 | 6.39 | 7.60 |
| Order 5 | 3.04 | 3.61 |
| Order 6 | 2.79 | 3.32 |
| Total | 26.24 | 31.2 |
For the emission intensity of the trip: